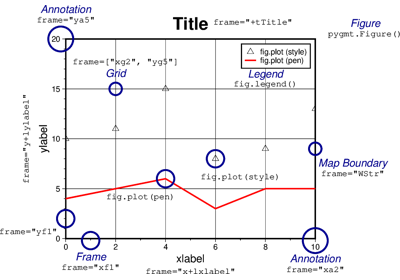
pygmt.Figure.legend
- Figure.legend(spec=None, projection=None, region=None, position='JTR+jTR+o0.2c', box=False, verbose=False, panel=False, transparency=None, perspective=False, **kwargs)
Plot a legend.
Makes legends that can be overlaid on maps. Reads specific legend-related information from an input file, or automatically creates legend entries from plotted symbols that have labels. Unless otherwise noted, annotations will be made using the primary annotation font and size in effect (i.e., FONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY).
Full GMT docs at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/6.6/legend.html.
Aliases:
D = position
F = box
J = projection
R = region
V = verbose
c = panel
p = perspective
t = transparency
- Parameters:
spec (
str|PathLike|StringIO|None, default:None) –The legend specification. It can be:
Nonewhich means using the automatically generated legend specification filePath to the legend specification file
A
io.StringIOobject containing the legend specification
See https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/6.6/legend.html for the definition of the legend specification.
projection (
str|None, default:None) – projcode[projparams/]width|scale. Select map projection.region (str or list) – xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax[+r][+uunit]. Specify the region of interest.
position (str) – [g|j|J|n|x]refpoint+wwidth[/height][+jjustify][+lspacing][+odx[/dy]]. Define the reference point on the map for the legend. By default, uses JTR+jTR+o0.2c which places the legend at the top-right corner inside the map frame, with a 0.2 cm offset.
box (
Box|bool, default:False) – Draw a background box behind the legend. If set toTrue, a simple rectangular box is drawn using MAP_FRAME_PEN. To customize the box appearance, pass apygmt.params.Boxobject to control style, fill, pen, and other box properties.verbose (bool or str) – Select verbosity level [Full usage].
panel (
int|Sequence[int] |bool, default:False) –Select a specific subplot panel. Only allowed when used in
Figure.subplotmode.Trueto advance to the next panel in the selected order.index to specify the index of the desired panel.
(row, col) to specify the row and column of the desired panel.
The panel order is determined by the
Figure.subplotmethod. row, col and index all start at 0.perspective (
float|Sequence[float] |str|bool, default:False) –Select perspective view and set the azimuth and elevation of the viewpoint.
Accepts a single value or a sequence of two or three values: azimuth, (azimuth, elevation), or (azimuth, elevation, zlevel).
azimuth: Azimuth angle of the viewpoint in degrees [Default is 180, i.e., looking from south to north].
elevation: Elevation angle of the viewpoint above the horizon [Default is 90, i.e., looking straight down at nadir].
zlevel: Z-level at which 2-D elements (e.g., the map frame) are drawn. Only applied when used together with
zsizeorzscale. [Default is at the bottom of the z-axis].
Alternatively, set
perspective=Trueto reuse the perspective setting from the previous plotting method, or pass a string following the full GMT syntax for finer control (e.g., adding+wor+vmodifiers to select an axis location other than the plot origin). See https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/6.6/gmt.html#perspective-full for details.transparency (float) – Set transparency level, in [0-100] percent range [Default is
0, i.e., opaque]. Only visible when PDF or raster format output is selected. Only the PNG format selection adds a transparency layer in the image (for further processing).